HYPOPITUITARISM
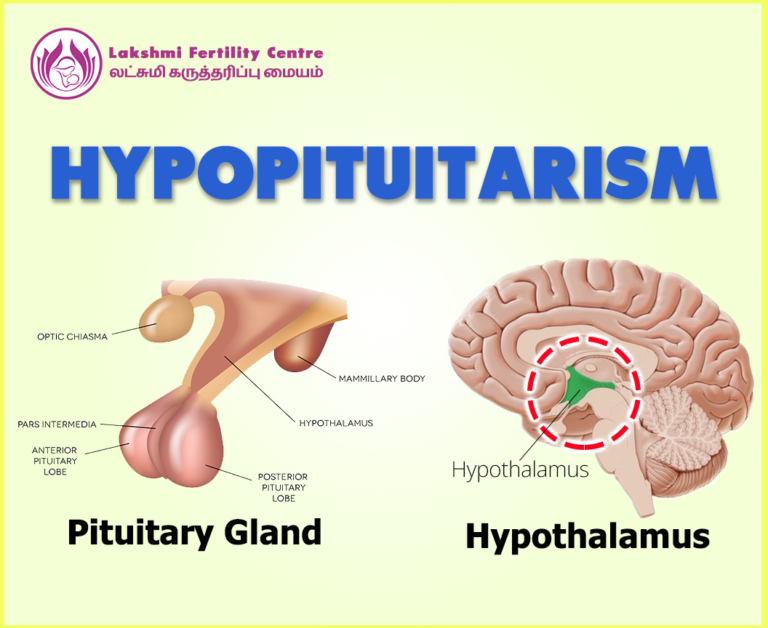
The pituitary gland sits just below your hypothalamus. It consists of two lobes, called the anterior pituitary and posterior pituitary. The hypothalamus is connected to and communicates with the anterior lobe through a network of blood vessels. It communicates with the posterior lobe by tissue called the pituitary stalk. The hypothalamus sends signals in the form of releasing hormones to tell the anterior and posterior pituitary when to release and secrete its hormones. Malfunctioning of these glands leads to Hypopituitarism which may damage the chance of getting pregnant and maintain fertility.
SYMPTOMS OF HYPOPITUITARISM:
- Hot flashes in the upper body, usually more intense in face, neck and chest.
- Irregular periods or no periods.
- Loss of pubic hair.
- Less production of milk for breastfeeding.
- Decreased facial or body hair.
- Mood swings.
- Fatigue.
- Unusual urination and extreme thirst.
- Imbalances in minerals such as sodium and potassium, known as electrolytes.
MEDICATIONS:
Treatment for hypopituitarism depends on which pituitary hormones are deficient and the cause of the hypopituitarism. For those reasons, treatments are very individualized. The healthcare team will determine the best treatment plan according to the symptoms. Common treatment options for hypopituitarism include:
-
HORMONE REPLACEMENT THERAPY:
Hormone replacement therapy aims to restore the deficient pituitary hormones to normal levels.
-
SURGERY:
Pituitary adenomas can cause hypopituitarism. Adenomas are tumors formed from glandular structures in epithelial tissue caused by genetic mutations. People who have pituitary adenomas may undergo surgery to remove the adenoma.
-
RADIATION THERAPY:
Some pituitary adenomas can be treated using radiation therapy.
