UTERINE FIBROIDS:
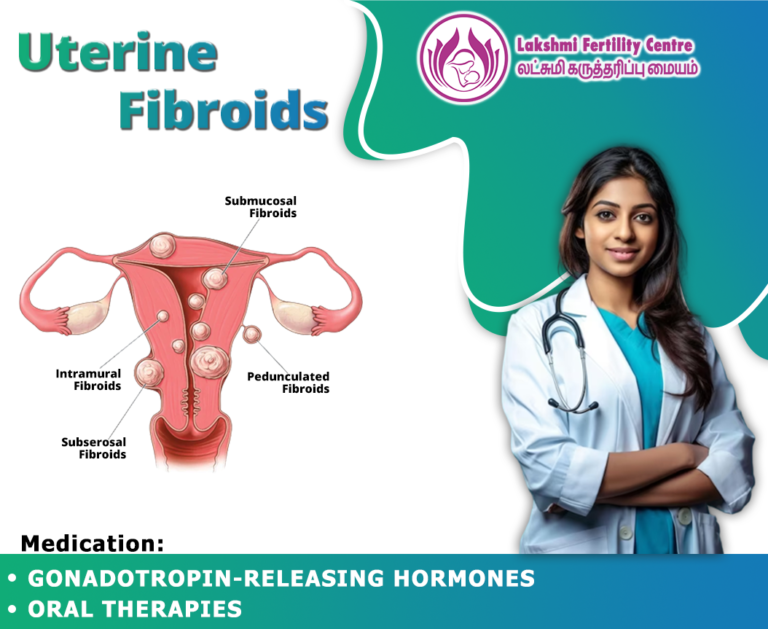
Uterine fibroids are growths in the uterus. They often appear during the years usually able to get pregnant and give birth. Uterine fibroids are not cancer, and almost never turn into cancer. They are not linked with higher risk of other types of cancer in the uterus either. They are also called leiomyomas or myomas. A fibroid can distort the inside and the outside of the uterus. In extreme cases, some fibroids grow large enough to fill the pelvis or stomach area. They can make a person look pregnant.The formation of fibroids cannot be identified, because they often cause no symptoms. A healthcare professional can find fibroids during a pelvic exam or pregnancy ultrasound.
SYMPTOMS OF UTERINE FIBROIDS:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding or painful periods.
- Longer or more frequent periods.
- Pelvic pressure or pain.
- Frequent urination or trouble during urination.
- Growth in stomach area.
- Constipation.
- Pain in the stomach area or lower back, or pain during intercourse.
MEDICATIONS:
-
GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONES:
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone medications work by shrinking fibroids. They sometimes used to shrink a fibroid before surgery, making it easier for removal. However, these medications are temporary, and if you stop taking them, the fibroids can grow back.
-
ORAL THERAPIES:
Elagolix is a new oral therapy to manage heavy uterine bleeding in women who haven’t experienced menopause with symptomatic uterine fibroids. It can be taken for up to 24 months. Another oral treatment known as tranexamic acid, treats heavy menstrual bleeding with uterine fibroids.
