Embryo Freezing: What You Need to Know
In recent years, embryo freezing has become a significant option for individuals and couples who want to preserve their fertility for the future. Whether it’s for personal, medical or professional reasons, embryo freezing offers a way to maintain the potential for future parenthood.
In this article, we explore what embryo freezing is, how the process is done and how it can help improve the chances of having a baby through IVF treatment.
What Is Embryo Freezing?
Embryo freezing, also called embryo cryopreservation, is a process where fertilized embryos are frozen for future use. It’s commonly used in IVF cycles, especially for those looking to preserve fertility or undergoing treatments like chemotherapy that may affect fertility. In this process, eggs are retrieved, fertilized with sperm and developed into embryos. The healthy embryos are then frozen and stored at sub-zero temperatures for later implantation.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), embryo freezing has become increasingly popular due to its safety and effectiveness. At Lakshmi Fertility Centre, we provide advanced embryo freezing services, ensuring the highest standards of care and technology to give you the best chance for parenthood when you’re ready.
Why Consider Embryo Freezing?
People consider embryo freezing for a variety of reasons:
- Fertility Preservation for Future Parenthood: Ideal for those who want to delay having children due to personal, career or medical reasons.
- Medical Treatments: Cancer treatments such as chemotherapy can damage reproductive organs, leading many cancer patients to freeze embryos before undergoing treatment.
- Excess Embryos from IVF: Couples undergoing IVF may have viable embryos left after the treatment cycle. These embryos can be frozen for future use.
- Age-related Fertility Decline: Women may choose to freeze embryos at a younger age to preserve their fertility for later in life when their natural fertility may decline.
As reported by Livestrong Fertility, embryo freezing provides patients with flexibility, preserving their options for starting a family when the time is right.
Process of Embryo Freezing
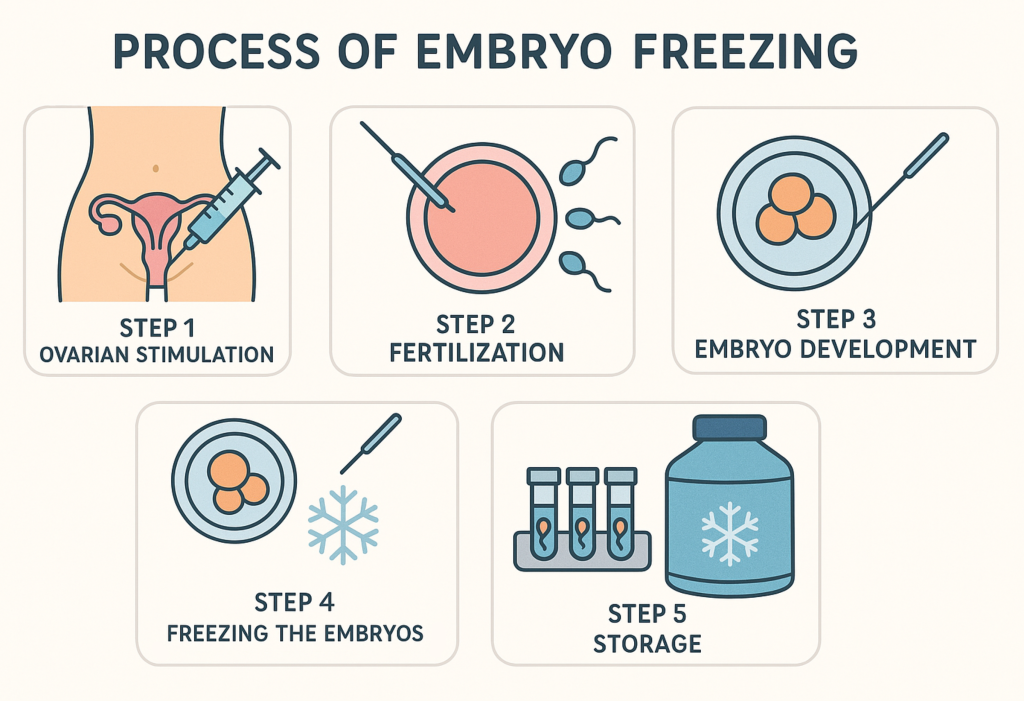
Step 1: Ovarian Stimulation
Before the embryo freezing procedure begins, the female patient undergoes ovarian stimulation. This involves hormone therapy to stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs, instead of the single egg produced in a normal menstrual cycle. These eggs are then retrieved from the ovaries.
Step 2: Fertilization
The eggs are fertilized in the laboratory using sperm from the male partner or a donor. In some cases, a technique called ICSI (Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection) may be used to inject a single sperm directly into each egg. This helps improve the chances of fertilization, especially in cases of male infertility.
Step 3: Embryo Development
The fertilized eggs or embryos, are cultured in a controlled environment for several days to allow them to develop. The embryologist monitors their growth and selects the best-quality embryos for freezing.
Step 4: Freezing the Embryos
Once the embryos are developed, they are frozen using a process called vitrification. This rapid freezing method helps prevent ice crystals from forming, ensuring that the embryos remain viable once thawed.
Step 5: Storage
The frozen embryos are then stored in liquid nitrogen at extremely low temperatures until the patient is ready to use them. These embryos can be stored for years without significant loss in quality.
How Is Embryo Freezing Used in IVF?
In IVF cycles, embryo freezing plays a crucial role in offering flexibility and multiple chances for conception. If the first IVF cycle doesn’t result in pregnancy, frozen embryos can be thawed and transferred during a subsequent cycle. This process is known as Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET).
Studies have shown that FET cycles can have success rates similar to or even better than fresh embryo transfers. This is largely because frozen embryos are often of higher quality since they are typically created using eggs from younger women who have undergone ovarian stimulation.
For more details on IVF success rates, refer to the CDC’s ART Data.
Benefits of Embryo Freezing
Embryo freezing offers several key benefits:
- Preservation of Fertility: Allows women and men to preserve their fertility for future use, especially useful for women who want to delay childbirth due to career, personal reasons or health concerns like undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
- Increased Success Rates: For couples undergoing IVF, embryo freezing can increase the chances of a successful pregnancy in the future. Embryos can be stored and used in subsequent IVF cycles, eliminating the need for repeated stimulation cycles.
- Minimizing Risks in Future Pregnancies: If embryos are frozen and stored properly, there is a reduced risk of complications during pregnancy. Using frozen embryos from a previous cycle can help avoid multiple IVF attempts, saving time, money and emotional strain.
- Flexibility for Family Planning: Couples who may not be ready for children immediately but want to ensure they have a healthy, viable option in the future can freeze embryos to use when the time is right.
- Gender Selection: For those interested in selecting the gender of their child, embryo freezing allows the option for pre-implantation genetic testing (PGT). This helps identify embryos with specific genetic traits, including gender, before implantation.
Risks and Considerations
While embryo freezing is a safe procedure, there are several factors to consider:
- Not all embryos survive the freezing and thawing process.
- It requires emotional and financial investment.
- The success of a frozen embryo transfer can depend on the quality of the embryo at the time of freezing and the age of the woman.
Success Rates of Embryo Freezing
Frozen embryo transfer (FET) success rates depend on several factors, including the woman’s age at the time of embryo freezing, the quality of the embryos and the clinic’s expertise. In general:
- For women under 35, the success rate for FET is typically around 30-50% per cycle.
- The chances of success decrease as the woman’s age increases.
- Embryos frozen at a younger age generally have higher pregnancy outcomes.
FAQs
1. How long can frozen embryos be stored?
Frozen embryos can be safely stored for 5 to 10 years or even longer, depending on the clinic’s regulations and the quality of the embryos.
2. Does freezing embryos reduce their quality?
Modern freezing methods such as vitrification preserve embryos with minimal cellular damage, maintaining their viability and increasing the success rates of future transfers.
3. What’s the best age to freeze embryos?
The best time to freeze embryos is in your 20s to early 30s, when egg quality is generally higher.
4. Can frozen embryos be used after many years?
Yes, many women have successfully conceived with embryos frozen for 10–15 years.
5. What’s the cost of embryo freezing?
The cost varies by clinic and location, but it typically includes the egg retrieval, fertilization, freezing and storage of embryos. Be sure to ask for clear pricing during your consultation.
Conclusion
If you’re considering fertility preservation or exploring IVF, Lakshmi Fertility Centre offers comprehensive care, personalized treatment plans and advanced technology to support your journey. Our team of experienced fertility specialists will guide you through every step of the process.
Contact us today to schedule a consultation and find out how embryo freezing can help you preserve your fertility for future parenthood.
