CHRONIC ANOVULATION
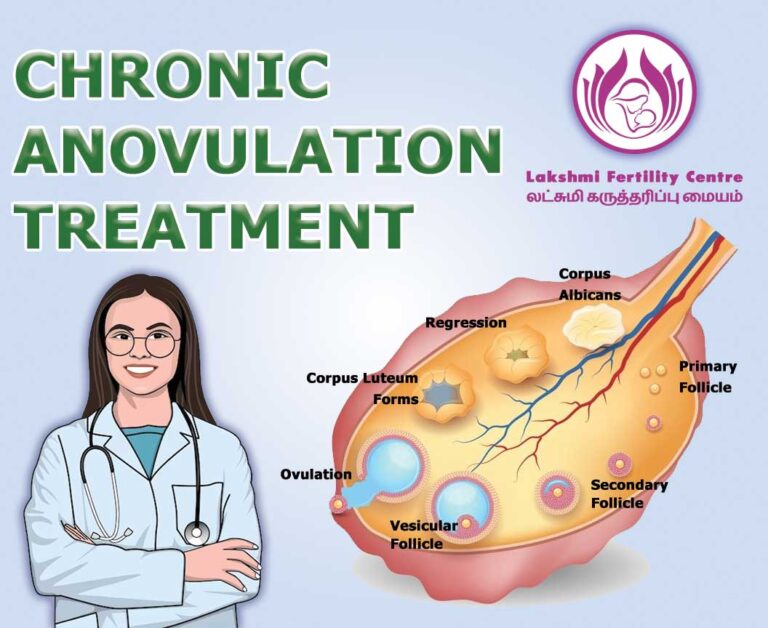
Chronic anovulation happens when an egg (ovum) doesn’t release from the ovary during the menstrual cycle. An egg is needed to have a pregnancy. The process of ovulation begins when your hypothalamus (a part of your brain) releases Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH). GnRH causes your pituitary gland (a gland in your brain) to secrete Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) and Luteinizing Hormone (LH). Chronic anovulation is a result of an imbalance of hormones that cause a woman to ovulate and may be part of the condition polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Irregular menstruation can also indicate anovulation, and we have a variety of diagnostic tools to help determine the cause of irregular cycles. It has the following indications to be nursed immediately.
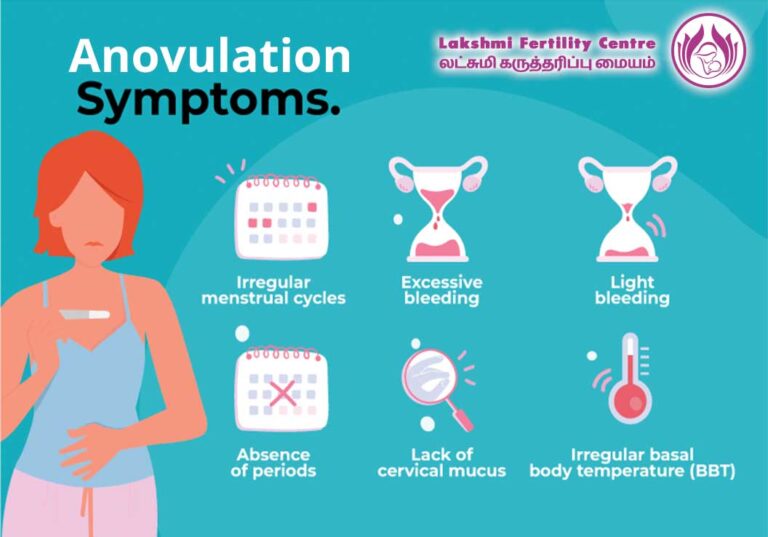
SYMPTOMS OF CHRONIC ANOVULATION:
-
IRREGULAR PERIODS:
If the length of time in between your periods keeps changing, it’s considered an irregular period. The average menstrual cycle is 28 days, but changing a couple of days shorter or longer than that should be noted.
-
HEAVY OR LIGHT PERIODS:
A heavy period is defined by losing over 80 ml of blood within your period and/or having a period that lasts longer than seven days. Blood loss of fewer than 20 ml throughout your period is considered a light period.
-
LACK OF PERIODS:
Missing one or more periods without being pregnant could be a sign of anovulation. It is also known as amenorrhea.
-
LACK OF CERVICAL MUCUS:
Right before and during ovulation, you usually have the most vaginal discharge called cervical mucus. It usually looks like raw egg whites. If you don't have this discharge, it is the symptom of anovulation.
-
IRREGULAR BASAL BODY TEMPERATURE:
Your basal body temperature is the actual temperature when you are at rest. It’s usually taken after you wake up and before you’ve done any type of physical movement or activity. Ovulation can cause a slight increase in your basal body temperature.
MEDICATIONS:
Most of the time, the medications used for treating anovulation are fertility drugs.
-
CLOMIPHENE CITRATE:
This medication helps to correct ovulatory irregularities and is a selective estrogen receptor modulator found to be effective in inducing ovulation in nearly 80% of the cases.
-
HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN INJECTION:
This hormone causes your ovary to release an egg. A synthetic form of it can be injected to help treat anovulation. It’s often taken with clomiphene citrate.
-
FOLLICLE STIMULATING HORMONE INJECTION:
If your body isn’t making enough FSH or if the other treatments for anovulation haven’t worked, your healthcare provider may have you get an injection of synthetic FSH to help your ovary release an egg.
-
GONADOTROPIN-RELEASING HORMONE AGONISTS AND ANTAGONISTS INJECTIONS:
An injection of GnRH agonists and antagonists helps to control the levels of luteinizing hormone (LH) your body secretes, which is the most needed one for ovulation.
